Human growth hormone (HGH) Somatropin in Sport
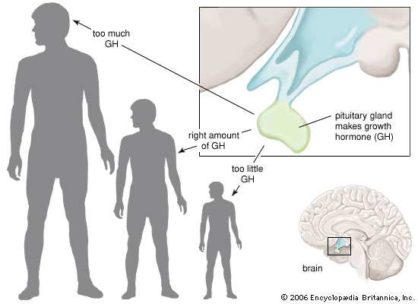
Human growth hormone is a natural substance that is secreted by the pituitary gland. This is important for adequate and timely growth, as well as human development from early childhood. Growth hormone (HGH) is secreted by the pituitary gland from birth and continues to peak levels reached in late adolescence. It is known that in the 2nd decade of human life, the level of HGH gradually decreases. For more than 40 years, somatotropic growth hormone has been available for the treatment of diseases that cause growth deficiency caused by chronic renal failure, Turner’s syndrome. HGH therapy is also possible as a treatment for growth hormone deficiency associated with the presence of pituitary tumors. Another recent approved use for growth hormone has been in the treatment of adults who suffer from AIDS wasting syndrome.
However, over the past three decades, growth hormones have enjoyed unprecedented market success for other reasons. Older and middle-aged people seem to believe that HGH can slow or stop aging. Athletes and young people want to improve their body condition and be more physically fit and perform better. Of all the stimulants abused by athletes, growth hormone is probably in the top three. Growth hormone in sports is like a drug of abuse. This is especially true for weightlifters or bodybuilders, where it is usually used in combination with androgenic steroids.
O Somatropin in history
In 1944, Somatotropin was obtained from the pituitary glands of animals by scientists, in other words, growth hormone. Further, in 1956, human Somatotropin was discovered. A year later, its clinical effectiveness was proven. The very first scandal associated with the use of somatotropin happened with the Italian sprinter Mennea, after which many others began to be convicted of this. Somatotropin is popular among different circles of society and interests. They talk about him, they are interested in him, and opinions are also divided.
After peak growth hormone impulses are reached (during the adolescent growth spurt), the impulse amplitudes gradually decrease with age. Although the release frequency continues to be the same, it increases during sleep and exercise.
Forms of Spomatropin
It is terrible to imagine that in the 80s there was only somatotropin extracted from the pituitary gland of a deceased person. But, after five years, those who took such growth hormone showed a rare Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, which is an encephalitis in a chronic and progressive form. The outcome of such a disease was a mental breakdown and death, so growth hormone derived from corpses was stopped. The only exception is a single Lithuanian company.
To date, somatotropin preparations can be safely divided according to the methods of their preparation into the following:
homologous – from the pituitary gland of a deceased person;
synthetic – in the composition they have more than 1 amino acid than human growth hormone;
recombinant – the fruit of the work of genetic engineers (the highest quality somatotropin).
Growth Hormone in bodybuilding
When you take growth hormone for bodybuilding, the HGH produced by the body stimulates a number of effects on your muscles. As your muscle mass grows, muscle tissue begins to work. As your fat is being burned, you will have more energy to work at an even higher level than before.
As you begin to climb to new levels of stress, HGH will greatly aid in muscle recovery. This hormone boosts immunity and healing, which means old injuries will be less of a concern. If you get new injuries, HGH will speed up the healing time.
Growth hormones affect lipid, protein and glucose metabolism. Boluses of fibrinogenic doses of growth hormone activate lipolysis and increase circulating non-esterified fatty acids (NEFA). This suggests a switch from carbohydrate to lipid sources of energy and may result in some reductions in total fat as well as weight gain. The effect on carbohydrate metabolism depends on the duration of growth hormone exposure and circulating NEFA levels. These include: increased hepatic glucose production, impaired peripheral glucose uptake, inhibition of hepatic and skeletal muscle glycogen storage, increased peripheral insulin resistance, and impaired glucose tolerance. Protein synthesis is increased in skeletal muscle through increased intracellular signaling and transcription with decreased protein oxidation after exercise, indicating a net anabolic effect on whole body metabolism.
From the foregoing, it is not difficult to conclude that the use of growth hormone:
- increase muscle mass and bone density
- reduce body fat
- increase physical activity
- increase cardiovascular tolerance to stress/exercise
What about Somatropin the most common claimin positive effects are:
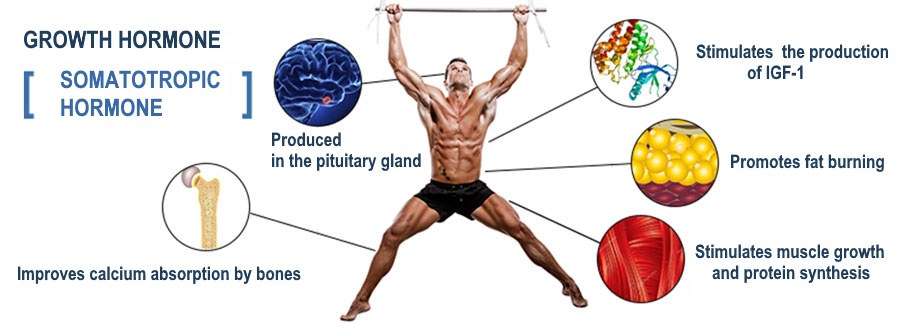
- Stimulates the production of IGF-1
- Produced in the pituitary gland
- Improves calcium absorption by bones
- Promotes fat burning
- Stimulates muscle growth and protein synthesis
Dosage and Usage
What is growth hormone and why it is needed is already clear. Now, you need to understand how to take it. Growth hormone is never taken orally. It is always administered as an injection, either subcutaneously or intramuscularly. Growth hormone acts fairly quickly once it is absorbed into the bloodstream. HGH dosing is still not fully known. While recent research suggests that it should be based on IGF levels, many physicians dose it based on body weight. For adults, the dosage is about 0.01-0.1 mg/kg body weight. This dosing depends on the type of product and what it is to be used for.
Somatotropin is produced in the form of a powder of a very light shade. The powder is contained in a metered bottle, which comes with a solution for dilution. When you mix these two components, the prepared solution must be immediately introduced so that it does not deteriorate. Growth hormone is best preserved at low temperatures, so it would be logical to store the package with the drug in the refrigerator.
Side effects
With the use of growth hormone in sports, there is a constant risk of overdose, as this may not be controlled by a professional. An overdose can lead to the development of devastating conditions caused by excessive production of growth hormone, such as acromegaly. Since HGH stimulates cell growth, there is also a risk that it may activate the proliferation of unwanted cells, such as cancer cells, causing the development of leukemia, prostate cancer, and malignant tumors. Comparatively less serious side effects of growth hormone include fluid retention and joint pain.
HGH can cause several side effects that are cause for concern. The most common are:
- Generalized edema
- carpal tunnel syndrome
- muscle pain
- Neuropathy (numbness and tingling)
- Increased blood glucose levels, diabetes
You must carefully weigh the risks and benefits of using the drug before deciding on a potentially dangerous therapy.
The widespread abuse of HGH has led to regulations restricting its sale and distribution. HGH is now recognized by the World Anti-Doping Agency and the International Olympic Committee as a performance-enhancing drug that prohibits athletes from using it.